Comparative analysis on mechanical and physical properties of jute-banana fiber reinforced epoxy-based hybrid composites: impact of fiber orientation
Downloads
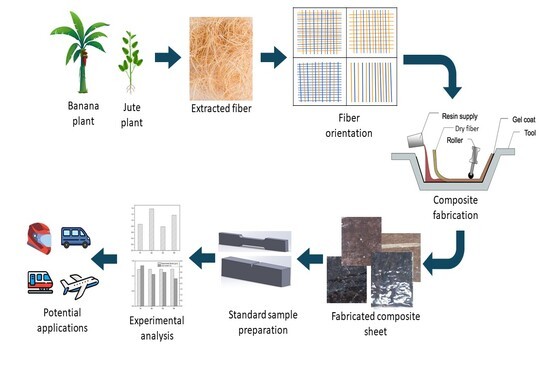
Natural fibers are eco-friendly and an alternative to synthetic fibers. In this study, a hybrid epoxy-based composite reinforced with jute and banana fibers with their different orientation [ J(Uni)-B(Uni), J(Uni)- B(Bi), J(Bi)-B(Uni), J(Bi)-B(Bi) ] matrix was evaluated. This research experimentally investigated the physical and mechanical properties, such as theoretical and experimental density, void content, water absorption, tensile strength, impact resistance, and hardness, by varying fiber orientation in the matrix. Key findings demonstrate that fiber orientation significantly influences the mechanical properties and microstructure of the composite. Specifically, orientation has a notably enhanced effect on tensile strength, hardness, and impact resistance, while conversely exhibiting a reduced influence on void formation within the matrix. Among the tested configurations, sample S4, featuring unidirectionally oriented Jute and Banana fibers, delivered the highest tensile strength (53.72 MPa) and hardness (58 HRM), coupled with the lowest observed void content (2.44%). Furthermore, sample S3, combining unidirectional Jute with bidirectional Banana fibers, achieved superior impact resistance (30.86 KJ/m²) compared to other orientations, while also maintaining the lowest level of hydrophilicity (0.79%). These composites have the potential to be an option for material choice that can be used in a high-strength and impact scenario.
K. Mylsamy and I. Rajendran, “The mechanical properties, deformation and thermomechanical properties of alkali treated and untreated Agave continuous fibre reinforced epoxy composites,” Mater. Des., vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 3076–3084, May 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.12.051.
J. Stanzione and J. La Scala, “Sustainable polymers and polymer science: Dedicated to the life and work of Richard P. Wool,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., vol. 133, no. 45, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1002/app.44212.
L. Kerni, S. Singh, A. Patnaik, and N. Kumar, “A review on natural fiber reinforced composites,” Mater. Today Proc., vol. 28, pp. 1616–1621, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.851.
T. Sathishkumar, P. Navaneethakrishnan, S. Shankar, R. Rajasekar, and N. Rajini, “Characterization of natural fiber and composites – A review,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., vol. 32, no. 19, pp. 1457–1476, Oct. 2013, doi: 10.1177/0731684413495322.
B. Shivamurthy, N. Naik, B. H. S. Thimappa, and R. Bhat, “Mechanical property evaluation of alkali-treated jute fiber reinforced bio-epoxy composite materials,” Mater. Today Proc., vol. 28, pp. 2116–2120, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.016.
D. Shanmugam and M. Thiruchitrambalam, “Static and dynamic mechanical properties of alkali treated unidirectional continuous Palmyra Palm Leaf Stalk Fiber/jute fiber reinforced hybrid polyester composites,” Mater. Des., vol. 50, pp. 533–542, Sep. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.048.
N. Venkateshwaran and A. Elayaperumal, “Banana Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites - A Review,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., vol. 29, no. 15, pp. 2387–2396, Aug. 2010, doi: 10.1177/0731684409360578.
V. S. Srinivasan, S. Rajendra Boopathy, D. Sangeetha, and B. Vijaya Ramnath, “Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties of banana–flax based natural fibre composite,” Mater. Des., vol. 60, pp. 620–627, Aug. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.03.014.
M. Jannah, M. Mariatti, A. Abu Bakar, and H. P. S. Abdul Khalil, “Effect of Chemical Surface Modifications on the Properties of Woven Banana-Reinforced Unsaturated Polyester Composites,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 1519–1532, Jun. 2009, doi: 10.1177/0731684408090366.
M. Boopalan, M. Niranjanaa, and M. J. Umapathy, “Study on the mechanical properties and thermal properties of jute and banana fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites,” Compos. Part B Eng., vol. 51, pp. 54–57, Aug. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.02.033.
S. Parbin, N. K. Waghmare, S. K. Singh, and S. Khan, “Mechanical properties of natural fiber reinforced epoxy composites: A review,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 152, pp. 375–379, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2019.05.003.
X. Chen, S. Chen, Z. Xu, J. Zhang, M. Miao, and D. Zhang, “Degradable and recyclable bio-based thermoset epoxy resins,” Green Chem., vol. 22, no. 13, pp. 4187–4198, 2020, doi: 10.1039/D0GC01250E.
A. K. Bledzki, M. Urbaniak, A. Boettcher, C. Berger, and R. Pilawka, “Bio-Based Epoxies and Composites for Technical Applications,” Key Eng. Mater., vol. 559, pp. 1–6, Jun. 2013, doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.559.1.
A. Gopinath, M. S. Kumar, and A. Elayaperumal, “Experimental Investigations on Mechanical Properties Of Jute Fiber Reinforced Composites with Polyester and Epoxy Resin Matrices,” Procedia Eng., vol. 97, pp. 2052–2063, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.448.
M. Rezaur Rahman, M. Hasan, M. Monimul Huque, and M. Nazrul Islam, “Physico-Mechanical Properties of Jute Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 445–455, Feb. 2010, doi: 10.1177/0731684408098008.
M. Idicula, A. Boudenne, L. Umadevi, L. Ibos, Y. Candau, and S. Thomas, “Thermophysical properties of natural fibre reinforced polyester composites,” Compos. Sci. Technol., vol. 66, no. 15, pp. 2719–2725, Dec. 2006, doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.03.007.
Sachin S. Harak et al., “Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Areca and Abaca Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites,” J. Environ. Nanotechnol., vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 92–101, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.13074/jent.2024.12.244977.
K. C. Sekhar, M. S. Kumar, C. Polayya, and Y. Kowshikji, “Investigating the Influence of Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties of Composites Reinforced with Banana and Roselle Fibers,” Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 2214–2220, Mar. 2023, doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2023.49940.
R. Venkatesh, S. Raghuvaran, M. Vivekanandan, C. R. Kannan, T. Thirugnanasambandham, and A. Murugan, “Evaluation of Thermal Adsorption and Mechanical Behaviour of Intralaminar Jute/Sisal/E-Glass Fibre-Bonded Epoxy Hybrid Composite as an Insulator,” Adsorpt. Sci. Technol., vol. 2023, p. 9222562, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1155/2023/9222562.
V. Ganasan et al., “Mechanical, Moisture Absorption and Thermal Stability of Banana Fiber/Egg Shell Powder-Based Epoxy Composites,” in The International Conference on Processing and Performance of Materials (ICPPM 2023), Basel Switzerland: MDPI, Jan. 2024, p. 11. doi: 10.3390/engproc2024061011.
X. Li, L. G. Tabil, and S. Panigrahi, “Chemical Treatments of Natural Fiber for Use in Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review,” J. Polym. Environ., vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 25–33, Feb. 2007, doi: 10.1007/s10924-006-0042-3.
M. M. Hasan, M. A. Islam, and T. Hassan, “Analysis of jute-glass fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composite,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 24, p. e40924, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40924.
S. B. R. Devireddy and S. Biswas, “Physical and mechanical behavior of unidirectional banana/jute fiber reinforced epoxy based hybrid composites,” Polym. Compos., vol. 38, no. 7, pp. 1396–1403, Jul. 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23706.
M. Prashanth B H, P. S. S. Gouda, T. S. Manjunatha, N. R. Banapurmath, and A. Edacheriane, “Understanding the impact of fiber orientation on mechanical, interlaminar shear strength, and fracture properties of jute–banana hybrid composite laminates,” Polym. Compos., vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 5475–5489, Oct. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26239.
Rajkumar Bhati, Anant Prakash Agrawal, Shahazad Ali, and Abdhesh Kumar, “Synthesis and mechanical characterization of banana-hemp reinforced epoxy composites: Influence of fiber orientation,” J. Elastomers Plast., vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 559–579, Mar. 2025, doi: 10.1177/00952443251327735.
B. Dev et al., “Mechanical properties of unidirectional banana/snake plant fiber-reinforced epoxy hybrid composites: experimental and numerical analyses,” Polym. Bull., vol. 82, no. 8, pp. 3145–3174, 2025, doi: 10.1007/s00289-025-05658-x.