Supply of energy required for water-ammonia absorption refrigeration cycle for an industrial refrigerator using solar parabolic collectors and photovoltaic panels: case study Malaysia

Downloads
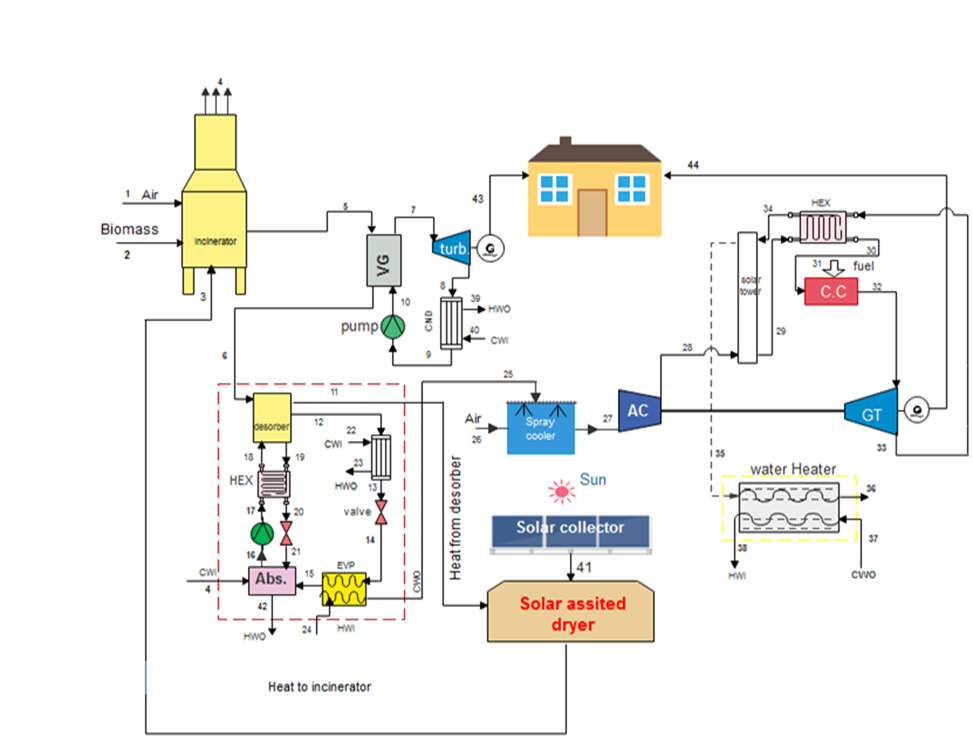
Conventional water-ammonia absorption refrigeration system in the industry uses heat energy generated by non-renewable energy sources such as the burning of natural gas, but it is just a matter of time before natural gas becomes depleted. Then, non-renewable energy often produces greenhouse gases that are harmful to the environment. Therefore, solar energy can be used as an alternative to supply the energy required by the absorption refrigeration cycle (ARC). Parabolic trough collectors (PTC) can supply the required heat energy to the reboiler, whereas photovoltaic (PV) panels can supply the electrical energy to the pump of an ARC. To prove the feasibility of using solar energy as a more sustainable alternative, a simulation of the PTC and PV models is conducted, and the average energy generated by each model is obtained. The result of this research proved that Malaysia is a suitable location for the implementation of solar technologies as the amount of solar radiation is sufficiently high throughout the year.
J. Abdulateef, M. Alghoul, A. Zaharim, and K. Sopian, “Experimental investigation on solar absorption refrigeration system in Malaysia,” Renew. Energy Sources, pp. 267–271, 2010.
Naderipour, A., Abdul-Malek, Z., Arshad, R.N., Kamyab, H., Chelliapan, S., Ashokkumar, V. and Tavalaei, J., 2021. Assessment of carbon footprint from transportation, electricity, water, and waste generation: towards utilisation of renewable energy sources. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 23, pp.183-201.
Wong, L.F., Afrouzi, H.N. and Tavalaei, J., 2024. Design and implementation of a dual-axis sun tracker for an Arduino-based micro-controller photovoltaic system. Future Technology, 3(3), pp.15-19.
Afrouzi, H.N., Mashak, S.V., Dastgheib, A.M. and Tavalaei, J., 2011, December. Economic Sizing of Solar Array for a Photovoltaic Building in Malaysia with Matlab. In 2011 First International Conference on Informatics and Computational Intelligence (pp. 306-311). IEEE.
Khavari, A.H., Abdul-Malek, Z., Moradi, M., Tavalaei, J., Abdolahzadeh Anbaran, S. and Wooi, C.L., 2016. An Economic Assessment of Hybrid Renewable Energy for a Remote Area Electrification in Iran. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 818, pp.151-155.
Zin, A.A.M., Moradi, M., Tavalaei, J., Naderipour, A., Khavari, A.H. and Moradi, M., 2017. Techno-economic analysis of stand-alone hybrid energy system for the electrification of Iran drilling oil rigs. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Computing Electronics and Control), 15(2), pp.746-755.
Wong, M., Afrouzi, H.N., Hassan, A., Jayamani, E., Tavalaei, J., Sunarso, J. and Mehranzamir, K., 2024. Design and Techno-Economic Analysis of a Hydrogen-Based Micro Hydro-Solar Hybrid Energy System for Sustainable Energy Access: A Case Study in Sri Aman, Sarawak.
Chieh, N.J.W., Afrouzi, H.N. and Tavalaei, J., 2023, December. Development of Integrated Structure of Hydrogen Production Using Photovoltaic Panels and Detailed Electrical Model for Electrolyser. In 2023 7th International Conference on Electronics, Materials Engineering & Nano-Technology (IEMENTech) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
M. S. Niasar, B. Ghorbani, M. Amidpour, and R. Hayati, “Developing a hybrid integrated structure of natural gas conversion to liquid fuels, absorption refrigeration cycle and multi effect desalination (exergy and economic analysis),” Energy, vol. 189, p. 116162, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116162.
S. A. Kalogirou, “Chapter three - Solar Energy Collectors,” in Solar Energy Engineering, Boston: Academic Press, 2009, pp. 121–217.
M. Marefati, M. Mehrpooya, and M. B. Shafii, “Optical and thermal analysis of a parabolic trough solar collector for production of thermal energy in different climates in Iran with comparison between the conventional nanofluids,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 175, pp. 294–313, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.080.
T. Khatib and W. Elmenreich, Modeling of Photovoltaic Systems Using MATLAB. 2016.
M. Tabassum, S. Kashem, and J. Ahmed, “Feasibility Study of Solar Power System in Residential Area,” vol. 5, pp. 10–17, May 2020.
R. Affandi, M. R. Ab Ghani, C. Gan, and Z. Jano, “A Review of Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) in Malaysian environment,” IJEAT, vol. 3, pp. 378–382, Jan. 2013.
T. K. Aseri, C. Sharma, and T. C. Kandpal, “Estimating capital cost of parabolic trough collector based concentrating solar power plants for financial appraisal: Approaches and a case study for India,” Renew. Energy, vol. 156, pp. 1117–1131, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.138.
Energysage, “The cost of solar panels in 2021: What price for solar can you expect?,” Energysage, 2021. https://news.energysage.com/how-much-does-the-average-solar-panel-installation-cost-in-the-u-s/ (accessed Oct. 05, 2021).
F. Baharum, M. H. Hassan, M. D. Sudirman, M. N. M. Nawi, and S. H. Ibrahim, “A comparative study of levelized cost of electricity between photovoltaic and concentrated solar powered power plants in Malaysia,” J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci., vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 134–145, 2018.