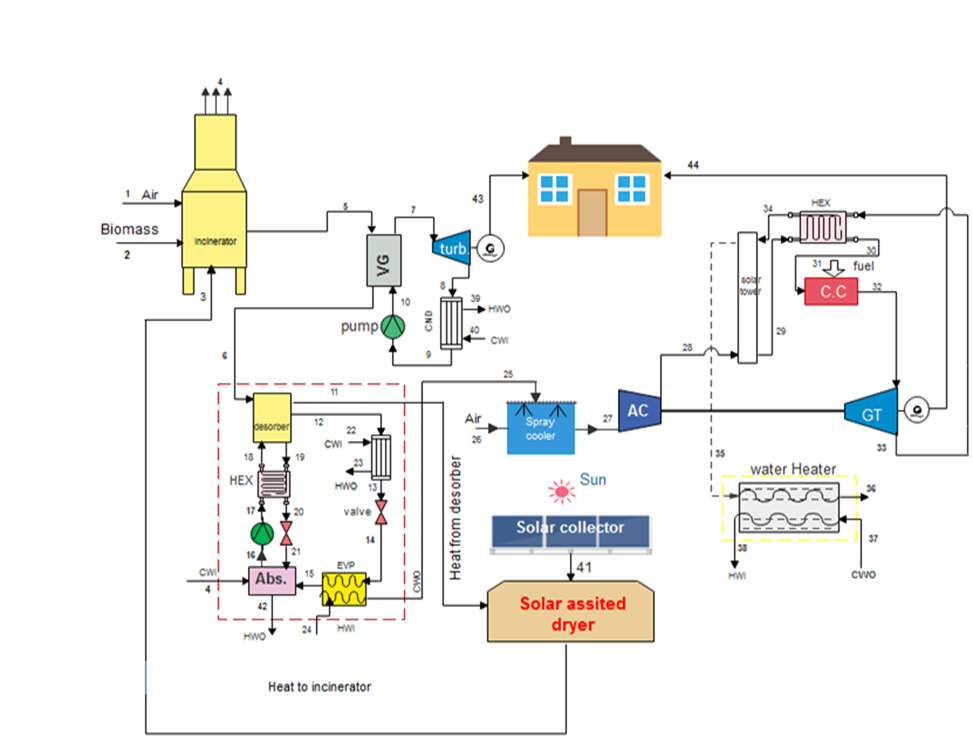
Integration of a biomass-fired thermal plant with solar-turbine and solar-assisted dryer for multi-energy generation
Downloads
The study analyzed the thermodynamics and environmental performance of a biomass-based solar-assisted trigeneration system for power, cooling, and hot water production. The system uses municipal waste in an incinerator and a solar tower with a gas turbine supplemented by natural gas. It includes an Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) for power, a vapor absorption system (VAS) for refrigeration, and a gas turbine. The analysis focused on thermodynamic, exergoeconomic, and thermo-environmental perspectives, considering indicators like the exergetic utility index (EUI), exergo thermal index (ETI), waste exergy ratio (WER), and sustainability index (SI). Simulation results show a net output of 6.128 MW, a cooling capacity of 131.1 kW, and a cooling water flow of 65.14 kg/s. The energy and exergy efficiencies are 66.68% and 53%, respectively. The solar tower helps reduce natural gas use by 633.6 kg/h, lowering carbon emissions. Exergy destruction is highest in the incinerator and combustion chamber. The exergoeconomic analysis shows minimal cost reduction in the gas turbine air compressor and incinerator. Thermo-environmental indicators were recorded as EUI 0.6992, ETI 0.9161, WER 1.092, and SI 0.6109, reflecting the system's environmental friendliness due to efficient energy use and low discharge temperatures.
C. Chen, M. Pinar, T. Stengos. (2020). Renewable energy consumption and economic growth nexus: Evidence from a threshold model. Energy Policy, 139(2020) 111295.doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111295.
F. I. Abam, O. E. Diemuodeke, E. B. Ekwe, M. Alghassab, O. D. Samuel, Khan, Z. A., et al. Exergoeconomic and environmental modeling of integrated Polygeneration power plant with biomass-based syngas supplemental firing. Energies 13(2020)6018-6027. doi:10.3390/en13226018.
F. Johnsson, J. Kjärstad, J. Rootzén, J. The threat to climate change mitigation posed by the abundance of fossil fuels. Climate Policy, (2018)1-17. doi:10.1080/14693062.2018.1483885.
J. G. J Olivier, J. A. H. W., Peters, K. M. Schure, K. M. Trends in global emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases: 2017 Report (PBL report no. 2674). PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, Bilthoven, the Netherlands.
D. Nikhil, A. Rajesh. Performance analysis of combined cycle power plant, Frontiers in Energy DOI 10.1007/s11708-015-0371-9.
C. C Oko, H. I. Njoku. Performance analysis of an integrated gas-, steam- and organic fluid-cycle thermal power plant. Energy, 122(2017)431-443.
Manente, G. (2016). High performance integrated solar combined cycles with minimum modifications to the combined cycle power plant design. Energy Conversion and Management, 111:186–97.
F. I. Abam, M. C. Ndukwu, O. I. Inah, O. D. Uchechukwu, M. Setiyo, O. D. Samuel, R. Uche. Thermodynamic modelling of a novel solar-ORC with bottoming ammonia-water absorption cycle (SORCAS) powered by a vapour compression refrigeration condensate for combined cooling and power, Mechanical Engineering for Society and Industry,.3(2) (2023)93-104.
A. E. Karaca, I. A. Dincer. A new integrated solar energy-based system for residential houses. Energy Conversion and Management, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113112.
B Sarkis, V. Zare, Proposal and analysis of two novel integrated configurations for hybrid solar-biomass power generation systems: Thermodynamic and economic evaluation. Energy Conv. Management, 160 (2018). 411-425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.01.061,
A. O Abdelhay, H. E. S. Fath, S. Nada. A. Solar-driven Polygeneration system for power, desalination, and cooling. Energy, 198(2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117341.
M. Sharifishourabi, T. Ratlamwala, H. Alimoradiyan, E. Sadeghizadeh. Performance assessment of a multigeneration system based on organic Rankine cycle. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering 3 (2016)225-232.
E. Bellos, C. Tzivanidis, C. Optimization of a solar-driven trigeneration system with nanofluid-based parabolic trough collectors. Energies, 10(2017).848-877.
A. Buonomano, F. Calise, A. Palombo, M. Vicidomini, M. Energy and economic analysis of geothermal–solar trigeneration systems: A case study for a hotel building in Ischia. Applied Energy, 138(2015).224-241.
S. Islam, I. Dincer, B. S. Yilbas, B. S. Energetic and exergetic performance analyses of a solar energy-based integrated system for multigeneration including thermoelectric generators. Energy, 93(2015)1246-1258.
B. Roshanzadeh, A. Asadi, G. Mohan. Technical and economic feasibility analysis of solar inlet air cooling systems for combined cycle power plants. Energies 16(2023)5352–5423. doi:10.3390/en16145352.
K. Owebor, C. O. C. Oko, E. O. Diemuodeke, O. J. Ogorure. Thermoenvironmental and economic analysis of an integrated municipal waste-to-energy solid oxide fuel cell, gas, steam, organic fluid- and absorption refrigeration cycle thermal power plants. Appl. Energy 239(2019)1385–1401. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.02.032
U. Sahoo, R. Kumar, P. C. Pant, R. Chaudhary. Development of an innovative Polygeneration process in hybrid solar-biomass system for combined power, cooling and desalination. Appl. Therm. Eng. 120 (2017) 560–567. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.034.
F I. Abam, V. Umeh, E. B. Ekwe, S. O. Effiom, J. Egbe, A. J. AnyandI, J. Enyia4, U. H. Ubauike, M. C. Ndukwu. Thermodynamic and environmental performance of a Kalina-based multigeneration cycle with biomass ancillary firing for power, water and hydrogen production. Future Technology 03 (01) (2024) 40-55.
F. I., Abam, B. B Okon, I. F Edem, M. C Ndukwu, E. B Ekpo, O. E. Diemuodeke, (2023). Environmental assessment and CO2 emissions of Brayton cycle configurations based on exergo-sustainability, economic and ecological efficiency using multi-criteria optimization technique. Future Technology, 3(1) (2023)1–12.
P. Ifaei, A. Ataei, C. Yoo. Thermoeconomic and environmental analyses of a low water consumption combined steam power plant and refrigeration Chillers-Part 2: Thermoeconomic an environmental analysis, Energy Convers Manage, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.06.030.
A. Bejan, G. Tsatsaronis (1995). Thermal design and optimization. Wiley, New York.
F I. Abam, B. B. Okon, E B Ekwe, J Isaac, S. O Effiom, M. C Ndukwu, O. I. Inah, P. A Ubi, S. Oyedepo, O. S Ohunakin. Thermoeconomic and exergoenvironmental sustainability of a power-cooling organic Rankine cycle with ejector system. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering, ElectronicsandEnergy2(2022)100064.
M. C. Ndukwu, M. I. Ibeh, P. Etim, C. U. Augustine, I. E. Ekop, A. Leonard, L. Oriaku, F. Abam, B. Lamrani, M. Simo-Tagne, L. Bennamoun. Assessment of eco‐thermal sustainability potential of a cluster of low‐cost solar dryer designs based on exergetic sustainability indicators and earned carbon credit. Cleaner Energy Systems, 3(2022)100027.